Roman Science
Science in Ancient Rome
The Ancient Romans made much advancement in the field of science. Below are several examples.

- Concrete
- Arch Structures
- Aqueducts
- Plumbing
- Machines
- Sundials
- Tools
- Glassblowing
- Military Technology

One of the greatest scientific feats of Ancient Rome is the concrete road. Nearly 30 military highways, all made of stone, exited the great city. At one point, 372 roads connected 113 provinces. Due to the concrete structure, many of these roads survived more than a thousand years.
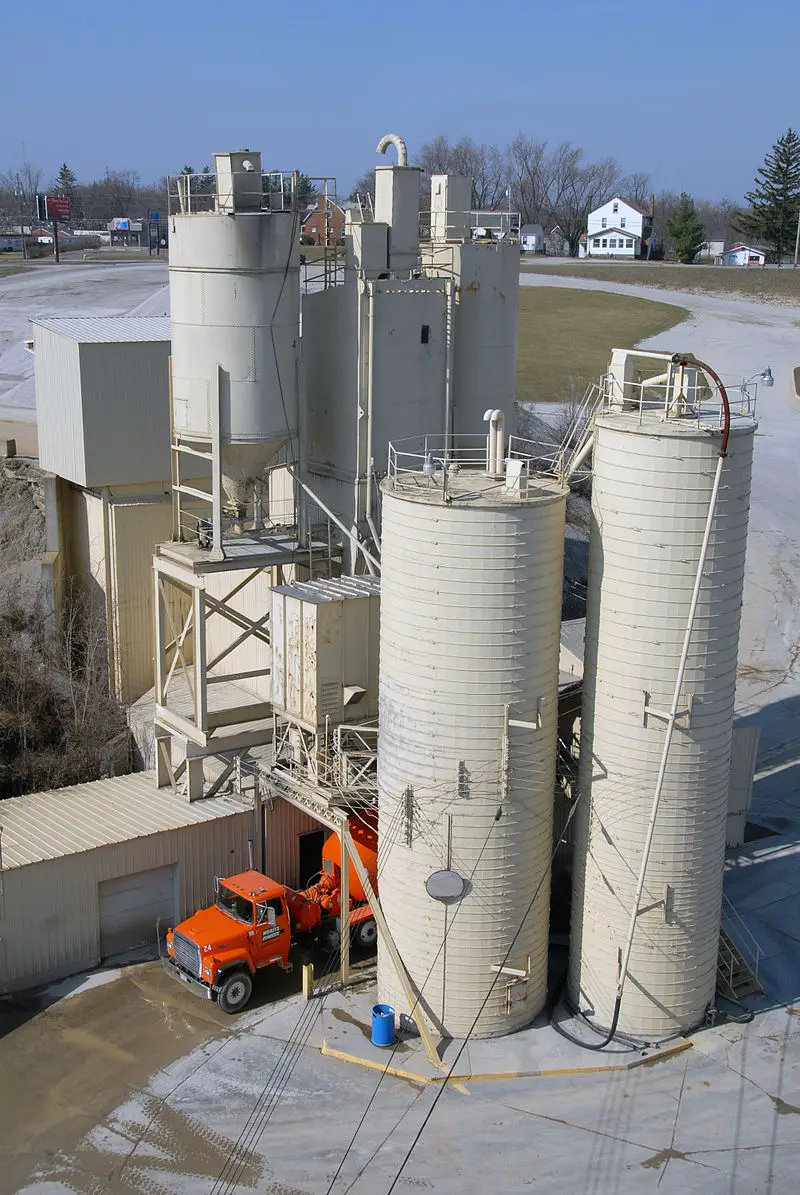

The Romans used the idea of the arch to create architecture that has continued to inspire builders even today. The discovery that the arch shape allowed weight to be distributed evenly allowed the Romans to create amazing buildings and homes. Arches were also used when developing aqueducts to deliver water to citizens all over Rome. Eleven aqueducts measuring nearly 220 total miles carried water across valleys and aided in the area’s

Citizens of Ancient Rome used sundials to tell time and even created portable versions. They also used tools that were quite advanced, such as measuring tools, manual drills, and metal spikes (used as nails)..
Advanced glassblowing techniques brought new technology to Rome in the form of window glass, hanging glass oil lamps, and other objects made of glass. Pliny the Elder, a key historian from Ancient Rome, also mentioned the use of mirrors in his writings.
Furthermore, Rome’s military benefited from technological improvements to weapons, shields, armor, and other items. Combined with the city’s ability to build roads and bridges, it is clear that Rome’s military success can be partially credited to its ability to excel in scientific fields.

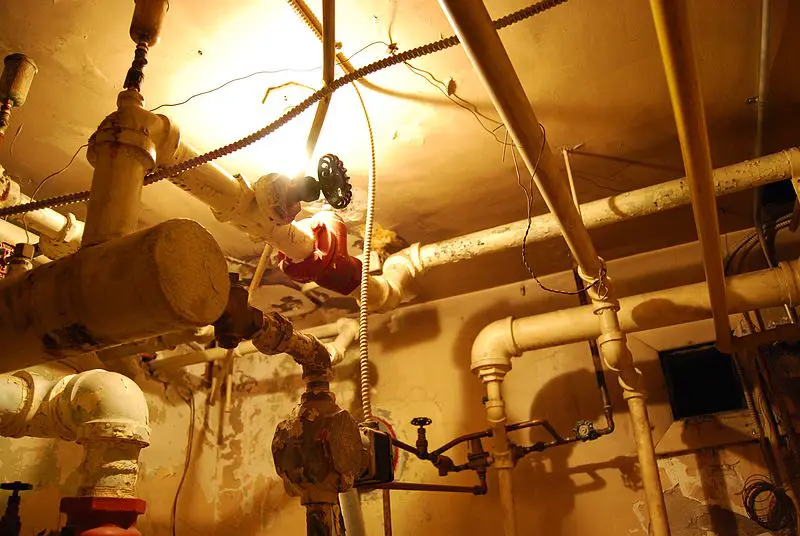
Some of the first flushing toilets and indoor plumbing systems were used in Rome. Some Roman homes contained sewer systems that carried waste to the Tiber River.

Romans used several different machines. For example, olive presses were used frequently. They also used various types of cranes to aid in constructing homes and buildings. Meanwhile, water power was also available through the invention of watermills, which helped grind corn, among other uses.

Throughout history, several Romans have been credited with significant scientific contributions, including:
- Galen
- Ptolemy
- Vitruvius
Galen was a surgeon and philosopher and once released a piece of writing titled “That the Best Physician is also a Philosopher.” Among other notable achievements, he was to discover the difference between dark and bright blood. Galen used animal subjects to learn more about the circulatory, respiratory, and nervous systems, among other parts of the body.
Claudius Ptolemy studied astronomy, geology, astrology, music, and other arts and sciences. He left behind several works, including Almagest, which includes a list of 48 constellations and a star catalog. In addition to an asteroid, craters on the Moon and Mars have been named in his honor.
Vitruvius is another writer whose work has provided us with important knowledge about Ancient Rome. He was also an architect and an engineer, so his writing has a unique perspective. He is sometimes referred to as the first architect, although this is likely due to the fact that his writings have survived. His texts include information about Rome’s machines, building materials, aqueducts, and much more.

Like the Greeks and other civilizations, the Romans dedicated many resources to the study of astronomy, astrology, geography, and other sciences. Their contributions were crucial to future generations and have helped us to collect the knowledge we have today.



